Documentation
Introduction
This documentation is meant to help you use the Project Planner.
About the Project Planner
The Project Planner at temperature-blanket.com is a tool for planning a crocheted or knitted project which incorporates weather data into its design. If you don’t know what a temperature blanket is, you can learn more here: What is a Temperature Blanket?
Use the Project Planner
Before you start working on your project, to help choose your yarn colors, plan your ranges, and preview your design
As you pick dates for your project, to view aggregated historical weather data or to get an idea what this year’s temperature ranges might be based on past temperatures
Before you buy your yarn, to estimate how many skeins of each colorway you might need
While you’re working on your project, to get historical weather data and get yarn color details
Don’t use the Project Planner
If your project contains dates beyond the current date
To view future weather forecasts. (For that use the Weather Forecast tool.)
If you are only looking to search for or match yarn colorways, use the stand-alone tool at temperature-blanket.com/yarn-colorway-finder.
Basics
Save Project
When you save a project, a shareable URL is created, and the project is saved in your browser's local storage. This web app does not store your project in a backend database. This means:
- There’s no need to set up an account in order to save your project
- You must save the project’s URL somewhere if you want to share the project or open it in a different browser.
To save your project, press the Save button at the top of the page. The project will be saved in your browser, and the project’s URL will be shown. Press Copy URL to copy the URL to your clipboard. If you want to share your project or open it in a different browser, make sure to save the URL in a place you can find it again later. You can also use the following keyboard shortcut to save your project:
| Cmd ⌘ + s or Ctrl + s | Save Project |
If you create a Project Gallery Page, your project is saved to a backend database, and you can re-open your project from its Project Gallery Page.
Your project must first have a valid location and dates in order to be saved, and it must first have weather data in order to save your project using the keyboard shortcut.
Open Project
Recently saved projects are stored in your browser’s local storage. Open the menu and select a project to load it’s settings and weather data.
You can also open any project by pasting the project’s URL in your browser’s address bar and opening the webpage. Press Search, and the project settings and weather data will be loaded.
Change Units
To change your project’s units between metric and imperial, from the top bar select °C / mm or °F / in. On smaller screens, press the three-dot menu icon, then choose your Units selection. On the Project Planner you can also use the following keyboard shortcut:
| u | Change Units |
Change Theme
To choose a theme for this site, press the Theme Switcher Icon at the top of the left menu, then select a theme in Light, Dark, or System mode. The System option will follow the light or dark preference of your device. On smaller screens, press the menu icon, then select the Theme Switcher button to change the theme. You can also use the following keyboard shortcut:
| t | Toggle Theme (Light, Dark, System) |
Undo/Redo
To undo or redo any previous edit to your project, press the Undo or Redo buttons at the top of the page. You can also use the following keyboard shortcuts:
| Cmd ⌘ + z or Ctrl + z | Undo |
| Cmd ⌘ + Shift ⇧ + z or Ctrl + Shift ⇧ + z | Redo |
Location
Choose a Location
Type a city, place, region, or landmark in the Location search box, then select a result from the autocomplete list.
You must choose an item from the suggested results. The suggested results come from geonames.org, and each item has a unique ID, latitude, and longitude which are used to find weather for that location. If your location is not in the suggested results, try again using a different nearby location.
Select Dates
For your location’s Duration, select either One Year or Custom.
- One Year – Select a Year, Month, and Day. The location’s weather data will start from that date and end one year later.
- Custom – Choose any From and To dates for the location’s weather data.
Selected dates should be in the past, not the future. Dates in the future will not contain any weather data. The maximum number of selected days per location is 370.
Multiple Locations
If you want to include weather data from multiple locations, press the Add Location button.
To remove a location, press the Remove Location icon.
The maximum number of locations per project is 200.
Location Errors
When you type your location in the search box, you might get a message saying:
“Whoah! There’s been a problem. It appears the location-fetching service is experiencing technical difficulties. You can refresh this webpage to see if the error has been resolved. If that doesn’t work, try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience.
This issue is caused when temperature-blanket.com can’t get location suggestion results from geonames.org. You can try refreshing the page, and if the error keeps occurring, try again later.
Weather
Weather Sources
Temperature-blanket.com provides several options from where to get weather data. To change the weather source settings, press the Weather Source button in the Location tab, Weather tab, or in the Project Menu.
Open-Meteo
The Open-Meteo database contains more than 60 years of weather data from a variety of open sources.
You can choose from the following Open-Meteo weather data models:
Best Match Default
1940 to present
~11 km, ~25 km, or 5 km resolution
Combines multiple models including ERA5 Land, ERA5, and CERRA (once real-time updates become available). Weather data may be altered by model upgrades. Model overview.
ERA5 Land Beta
1950 to present
~11 km resolution
Weather data is less likely to be altered, but there may be more missing weather data. Model overview.
ERA5 Beta
1940 to present
~25 km resolution
Weather data is less likely to be altered, but there may be more missing weather data. Model overview.
Weather data from Open-Meteo is licensed under Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0), and includes data from the Copernicus Program.
Meteostat
The Meteostat platform provides access to open data from thousands of weather stations world-wide. Measurements from the nearest stations are combined to produce an interpolated result. You can optionally choose to not fill missing weather with statistically optimized model data. (Filling missing weather data is on by default.)
Weather data from Meteostat is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0, with raw data provided by NOAA, DWD and others.
Daytime length calculations are by SunCalc licensed under BSD 2.
If your project has missing or incorrect weather data, you can also import or edit weather data.
All weather data is subject to change if the provider updates their models.
Get Weather Data
Once you’ve selected a location and dates, press the Search button to get weather data for your project. A request will be made to the weather source, and if there’s weather data available, it will be shown to you.
Grouping Weather Data
You can use daily weather data, or group it into weeks. Using weekly weather data can make your project shorter.
- Daily – Each day shows its own individual temperature, rain, snow, and daytime values.
- Weekly – Days are grouped into weeks which start on the day set from the
Weeks Start On setting. The weather data for each week is calculated
according to the following:
- High Temperature – The highest temperature of the week
- Average Temperature – The average temperature of the days in the week
- Low Temperature – The lowest temperature of the week
- Rain – The sum of rainfall of the days in the week
- Snow – The sum of snowfall of the days in the week
- Sun – The average daytime of the days in the week
The Average Temperature and Average Daytime of all items in your weather data (displayed above the weather chart) might be slightly different when using Daily vs Weekly weather data. This is an expected result because of how the averages are calculated.
View Weather Data
An overview of your project’s weather data is shown in a chart.
You can press the Show Color Details toggle to see color details in the weather chart.
Edit Weather Data
To edit weather data, your project’s weather grouping must be Daily, not Weekly. To edit weather data, press the value you want to change in the table under the weather chart. A modal will open where you can save the new value.
If you want to edit many values, it may be easier to work with the data in a spreadsheet:
- - Download your project’s weather data CSV file
- - Open the CSV file with a spreadsheet program (for example Microsoft Excel, Apple Numbers, or Google Sheets).
- - Edit the weather data you want to change, then export the document as a CSV file
- - Import the new CSV file into your project
Edited weather data is saved to your browser when you save your project. If you want to open your project in another browser, make sure to download your project’s weather data CSV file so you can import the CSV file to your project in that browser.
Import Weather Data
To import weather data, press the Import Weather Data button in the Weather tab; a modal will open where you can upload the CSV weather data file, then press Import to load the weather data into your project. Note that your project’s weather grouping must be Daily, not Weekly.
CSV File Requirements
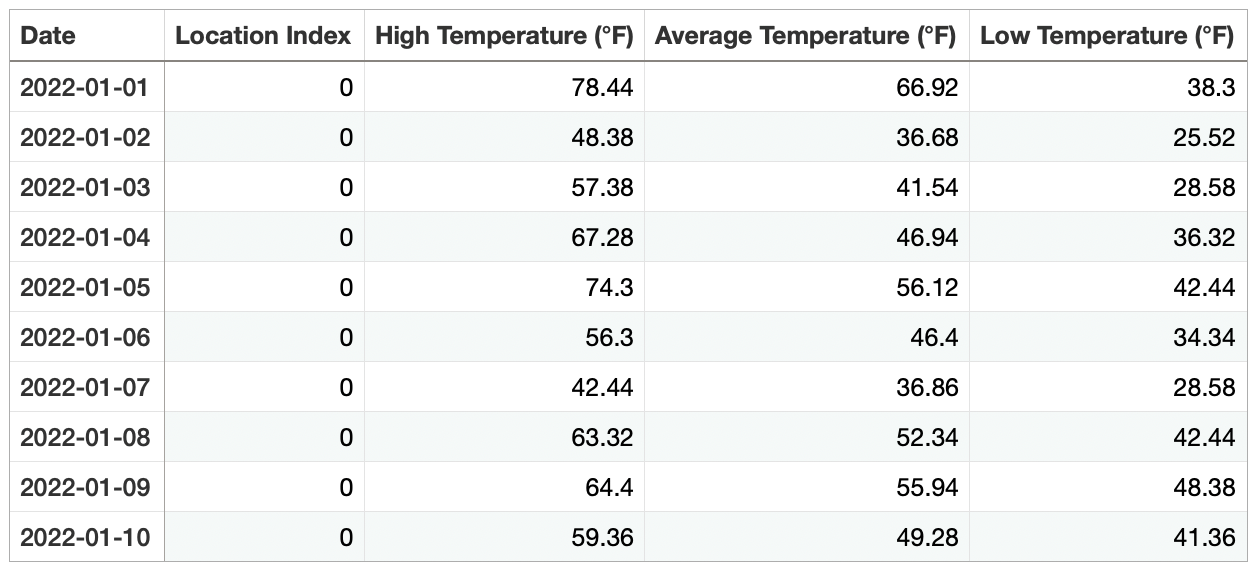
It’s simplest to download your project’s weather data CSV file and use that as a starting point for editing weather data.
But you can also import any CSV file with custom weather data (for example data from another weather source) as long as the file conforms to the following requirements:
Row 1 must contain the following two column headings:
- Date – Values in the Date column should be in the format of YYYY-MM-DD for best results, and must be in the range of dates selected for your project. Dates in the CSV file which are not dates selected for your project will be ignored.
- Location Index – Values in the Location Index column should be“0” (that’s a zero without the quotation marks) unless your project has more than one location. If your project has more than one location, the value should be the number of the location for which the date corresponds (0 is the first location, 1 is the second location, 2 is the third location, and so on).
Row 1 must contain any or all of the following weather data column headings. Use only column headings corresponding to your chosen units. Only columns with headings matching the following will be changed; other existing weather data will not be changed. Note the parentheses, spaces, symbols, and units.
- High Temperature (°F) or High Temperature (°C)
- Average Temperature (°F) or Average Temperature (°C)
- Low Temperature (°F) or Low Temperature (°C)
- Rain (in) or Rain (mm)
- Snow (in) or Snow (in)
- Daytime (h:m)
Values in the Daytime (h:m) column must be in the format of hours:minutes. For example, 08:12 means eight hours and twelve minutes..
For best results, save the CSV file with UTF-8 encoding.
Weather Errors
When you press the Search button, you might get a message saying:
Weather data not found. Please try a different location or dates.
If so, you’ll have to try to search again with a different location and/or selected dates.
- - Make sure your selected dates are in the past, not the future.
- - If your selected dates are from before about 1980, try more recent dates.
- - Try a different nearby location
Mixed Snow Parameters
Sometimes there might be a label below the Total Snowfall weather data which says Error: Mixed Parameters. This happens when there are multiple locations and multiple weather sources (Meteostat and Open-Meteo). The snow parameter from Meteostat measures the highest snow depth, and the snow parameter from Open-Meteo measures the total snowfall. When this data is combined—as happens in some cases when there are multiple locations and mixed weather sources—the Meteostat snow depth data gets treated as snowfall data instead, so the total snowfall amount will not be accurate. To get rid of the error message, make sure the weather source is Open-Meteo for all locations by changing the Weather Source to Open-Meteo (and optionally disabling the use of other weather sources if no data is found). There is currently no other way to prevent this issue. You can make projects with mixed snow parameters, just know that the snow data types will not be consistent.
Gauges
Add a Gauge
By default, every project has a Temperature Gauge, but you can also add other types of gauges in order to incorporate different types of weather data in your project. To add a gauge, press Select a Gauge, then select one of the available options.
Gauges you can create are:
- Temperature gauge (required)
- Rain gauge
- Snow gauge
- Daytime gauge
You can only add a gauge if the weather data contains that gauge’s information. For example, if there is no snow data, you won’t be able to add a snow gauge.
Gauge Direction
To change the direction of a gauge, press the Settings button, choose High to Low or Low to High, then press Save Settings.
- High to Low – Starting from the highest value, ranges decrease in value for each subsequent color.
- Low to High – Starting from the lowest value, ranges increase in value for each subsequent color.
Range Calculation Methods
There are four possible options used to determine which range a day’s weather value gets assigned to. Each method handles the inclusion or exclusion of specific temperature values differently.
- Include From, don’t include To (default): This method considers the temperature values starting from the specified From value, up to, but excluding, the specified To value. For example, if you set the range from 30 to 20 degrees, the range will include temperatures equal to or greater than 20 degrees, but not temperatures equal to or greater than 30 degrees. Ranges in a gauge using this method could look like this: 30 to 20, 20 to 10, 10 to 0…
- Include To, don’t include From: In contrast to the previous method, this approach includes temperature values up to and including the specified To value, but excludes temperatures equal to or less than the specified From value. For instance, if you set the range from 30 to 20 degrees, the calculation will include temperatures less than or equal to 30 degrees, but not temperatures less than or equal to 20 degrees. Ranges in a gauge using this method could look like this: 30 to 20, 20 to 10, 10 to 0…
- Include both From and To: This method includes temperature values starting from the specified From value and includes temperatures up to and including the specified To value. If you set the range from 30 to 20 degrees, the calculation will include temperatures equal to or greater than 20 degrees and temperatures equal to or less than 30 degrees. Ranges in a gauge using this method could look like this: 30 to 20.01, 20 to 10.01, 10 to 0.01…
- Don’t include From and To: As the name suggests, this method excludes both the specified From and To values from the calculation. If you set the range from 20 to 30 degrees, the calculation will exclude temperatures equal to or less than 20 degrees and temperatures equal to or greater than 30 degrees. Ranges in a gauge using this method could look like this: 30.01 to 20, 20.01 to 10, 10.01 to 0…
Here’s a table showing which values would be included in an example range from 13 degrees to 12 degrees.
| Option | Expression | Values in Range? |
|---|---|---|
| Include From, don’t include To (default) | From ≥ Range > To | 13 ✅ 12.5 ✅ 12 ❌ |
| Include To, don’t include From | From > Range ≥ To | 13 ❌ 12.5 ✅ 12 ✅ |
| Include both From and To | From ≥ Range ≥ To | 13 ✅ 12.5 ✅ 12 ✅ |
| Don’t include From and To | From > Range > To | 13 ❌ 12.5 ✅ 12 ❌ |
If you choose the third or fourth Range Calculation Method but don’t have Automatic Increments set or choose Round Increment (see below), temperature-blanket.com doesn’t currently auto-calculate optimal range From and To values. This may be addressed in a future update.
If a day’s weather value would fit in two or more ranges, the first-matching range (highest on the gauge) is used.
Increment Modes
A range increment is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a range.
- Automatic – Each range’s increment is automatically chosen based on your weather
data. The maximum and minimum weather data values for the gauge are
used to calculate increments which fit the number of colors.
- Round Increment – This option is available if an auto-calculated increment has decimals. Choose this option to avoid decimals in ranges’ From and To values.
- Manual – Set an increment value and a start value. Based on the Direction and the number of colors in your gauge, each range will be set using your increment value.
When using Automatic Increments on height-type gauges (Rain Gauge, Snow Gauge), depending on the weather data, some ranges might have negative values. If this is the case, you can manually adjust those ranges to positive values (in real life you can’t have a negative amount of rain or snow).
Adjust Ranges
To adjust an individual color’s range: select the Range; adjust the From and To values using the input fields, plus and minus buttons, or the range sliders; then press Save Range.
Color Tools
Preset Colors
To browse collection of preset colors to use in your project, press Browse Palettes. Then select a Category and change the filters to see different color combinations. Select the palette to use it in your project. The categories are as follows:
- Gallery – All user-made color palettes
- Featured – Popular user-made color palettes
- Schemes – Color schemes based on ColorBrewer2.org by Cynthia A. Brewer, Geography, Pennsylvania State University, licenced under Apache 2.
Image Palette
To create a palette of colors from an image, press the Image Palette button. Use a random image (from unsplash.com), or upload your own image. Click or tap the picture to select colors. Rearrange them or remove unwanted colors, then press Save to use the palette in your project.
Export/Import
To export a color palette as HTML color codes or yarn names, press Export/Import, then press Copy for whichever format you want. Share or paste the copied text somewhere you can find it later.
To import a color palette, press Export/Import, press the Import button, then type color names or paste a valid code or URL. When you're finished, press Save.
Sort Colors
To move a color in a palette, press the drag icon on the color and drag it to a new position in your gauge. You can also sort colors by pressing the Sort button, then choosing an option to sort all the colors by lightness or name. You can also reverse all the colors by pressing Reverse.
Yarn
Real yarn colors will look different than what’s on the screen. Any trademarked yarn or colorway details are owned by their respective companies. Purchases via links with a shopping cart icon support the developer of this web app at no extra cost to you. Colors may be inaccurate, and may not represent yarn as it appears in physical reality. Requests for yarn to be included in these results can be made by anyone using this request form.
Getting Yarn Colorway Data
This web app uses color approximations of real yarn colorways in order to display them as colors on your screen.
The process used to convert a real yarn colorway into a color on your screen is as follows:
- - An image of the colorway is found (usually from the brand or manufacture’s website).
- - A unobstructed area of the image showing as much color-variance as possible within that yarn colorway is chosen.
- - From the selected part of the image, the average color is generated as an HTML color code.
- - The HTML color code, colorway name, and link to the colorway’s webpage is saved in a database which this web app uses to display the colorway data.
Choose Yarn Colorways
To pick yarn colorways to use in your project, press the Choose Colorways button. Select the colorways you want to use, choose to add them to your existing palette or to create a new palette, then press Use These Colorways.
Preview
Create a Preview
To view and customize what your project might look like, select a Pattern Type and adjust the settings. These are the different pattern types which you can use to customize your preview:
- Calendar – Squares are arranged in a calendar-like grid, grouped by month.
- Chevrons – Zig-zag rows of stitches
- Continuous Square – Starting from the center, stitches are added in a clockwise square pattern. Possible crochet patterns: Granny Square, Moss Stitch/Linen Stitch Square.
- Corner to Corner – Lines are added in a back-and-forth pattern starting from the bottom right.
- Daytime Rows – Each row is split according to the duration of sunlight that day. Daytime stitches = d × r ∕ 24. Night stitches = r − Daytime stitches. d = Daytime (time from the day’s sunrise to sunset in hours). r is the total stitches per row. 24 is the number of hours in a day.
- Hexagon Rounds Each round in a hexagon represents one day. Hexagons are added from left to right, top to bottom.
- Month Rows – Rows are grouped by month from top to bottom or left to right. Months with fewer days have extra rows added, so that each month has the same number of rows.
- Month Squares – Each square represents one month. Each round in a square represents one day, starting with the first of the month in the center of the square. Months with fewer days have extra rounds added, so that each square has the same number of rounds.
- Rows – Straight rows of stitches
- Split Month Squares – Each square represents one month. Each round in a square represents one day, starting with the first of the month in the center of the square. Each round is split in half to represent two different weather parameters. Months with fewer days have extra rounds added, so that each square has the same number of rounds.
- Square Rounds – Each round in a square represents one day.
- Squares – Each square represents one day.
The project preview might not look like a real crochet or knitted item. It is only meant to give you an idea of using the colors and pattern type. Patterns are not provided.
Assigning SeasonsBeta
This feature is in beta, which means it may have unexpected issues or may have breaking changes in the future. If you encounter any issues or have feedback, please let the developer know. Here is the contact page.
Assigning seasons allows you to use different weather parameters for different times of the year. For example, you could use High Temperatures for Spring and Summer, and Low Temperatures for Fall (Autumn) and Winter.
To assign seasons, select the Seasons toggle in the settings of the Preview tab. Note that not all pattern types support seasons, so if you don't see the Seasons toggle, select a different pattern type.
To edit which dates are in which seasons, press the name of a season. You can choose from several preset options, or customize the start and end dates for each season.
Notes:
- - If a date falls outside of a custom defined seasons' ranges, that date will use the Accent Color as a fallback.
- - If two season's date ranges overlap, the first season which includes that date will be used. The order of the seasons is as follows: 1) Spring, 2) Summer, 3) Fall (Autumn), 4) Winter.
For now, only the Rows pattern type supports assigning seasons. Support for more pattern types may be added in future updates.
Gallery
Download
Download Gauges and Weather Data (PDF)
To download your color charts and weather data as a PDF file, press the three-dot menu icon, press the Download button, then press the Color Charts and Weather Data (PDF) button. You can also open the download menu by using the following keyboard shortcut:
| d | Open Download Menu |
Download Weather Data (CSV)
To download a CSV file with your project’s weather data, press the three-dot menu icon, press Download, then press Weather Data (CSV). You can also open the download menu by using the following keyboard shortcut:
| d | Open Download Menu |
Download Preview Image (PNG)
To download a PNG file of your project’s preview image, press the three-dot menu icon, press Download, then press Preview Image (PNG). You can also open the download menu by using the following keyboard shortcut:
| d | Open Download Menu |